Centralized ATM & Branch Physical Security Monitoring for 2026 and Beyond

Indian banks operate some of the most geographically diverse and environmentally demanding security networks in the world. Thousands of branches and ATMs span metros, Tier-2 towns, rural highways, and coastal regions—each with unique operational and environmental risks.
Today’s core challenge is not the absence of alarms.
It is the absence of centralized intelligence.
Fragmented security systems create:
An AIoT Security Intelligence Platform transforms physical security from isolated site-level alerts into a national command framework—with encrypted, real-time visibility, predictive maintenance, and automated compliance documentation.
For Indian banking CSOs, this is not a technology upgrade.
It is an operational risk modernization initiative.
Large Indian banks operate:
This infrastructure was built incrementally over decades.
The result:
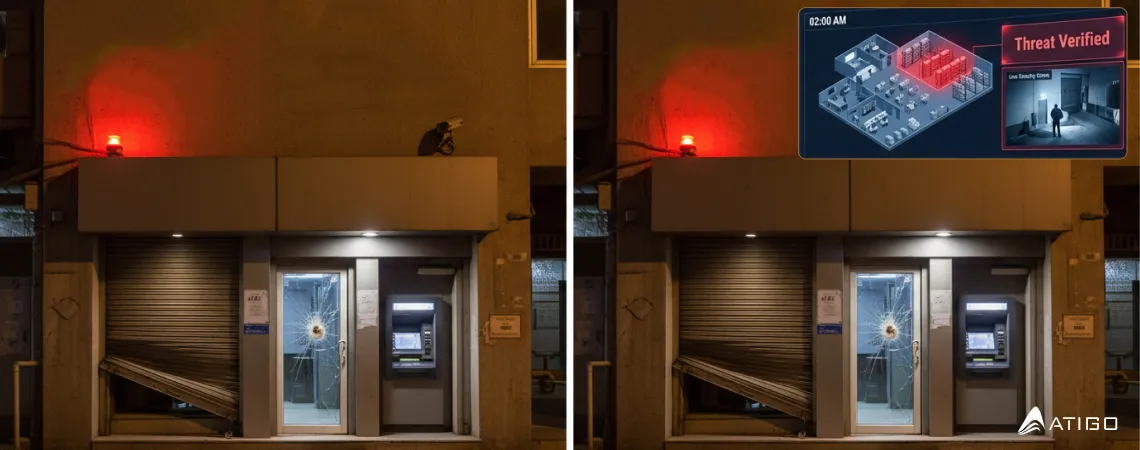
When an intrusion alert triggers at 2:37 AM in Pune, the key question is not:
“Did a sensor trigger?” It is:
Traditional alarm systems cannot answer these questions.
India presents unique operating conditions:
Over time, these factors contribute to:
Security risk in India is not only criminal.
It is environmental plus operational.
Without predictive intelligence, degradation becomes vulnerability.
Most banks still operate site-level alarm systems that:
This creates four systemic weaknesses:
1. Fragmented Visibility
No national dashboard. No macro threat analysis.
2. Alert Fatigue
Hundreds of false alarms per month across 100-location networks.
3. Reactive Detection
Alerts after intrusion has begun, not before damage occurs.
4. Maintenance Blind Spots
Failures discovered only during or after incidents.
Modern banking risk management requires a centralized control layer.
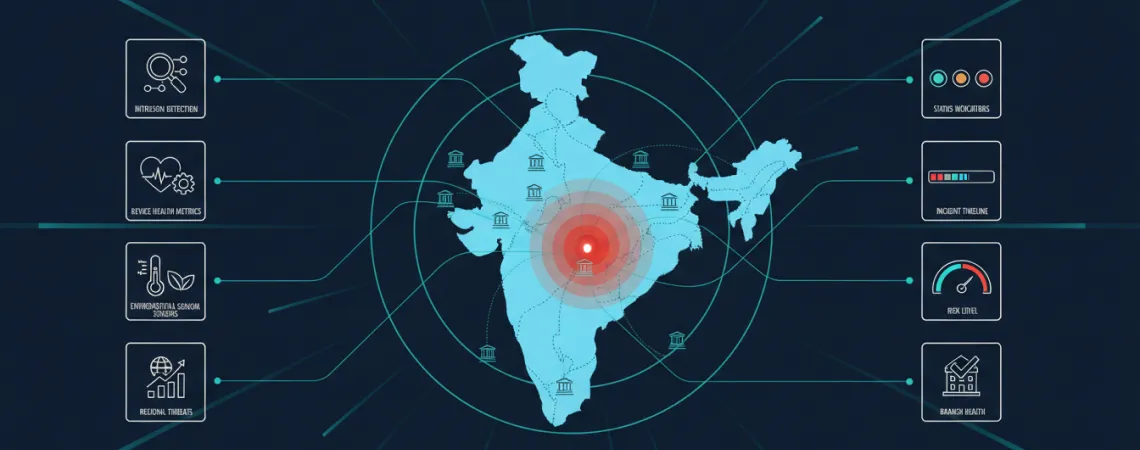
AIoT combines:
But at executive level, its value lies in architecture.
A single national dashboard aggregating:
From Kashmir to Kerala, every location becomes visible in real time.
Security infrastructure must itself be secure.
The platform uses:
For banking networks, encryption is not optional.
It is foundational.
The AI layer learns:
Instead of reacting to single triggers, the system:
This reduces false alarms by up to 60% while preserving high sensitivity to genuine threats.
Every device continuously reports:
The system predicts failure before outage
This eliminates:
For geographically distributed banks, predictive maintenance is operational resilience.
An AIoT platform converts security operations into a command framework.
For any branch or ATM:
This eliminates guesswork during 2 AM alerts.
RBI Master Directions emphasize:
While guidelines primarily focus on cyber resilience, physical security maturity directly influences regulatory posture.
The platform automatically generates:
Access audit trails
Audit preparation shifts from manual compilation to structured export.
For institutions that previously required significant manual effort per audit cycle, centralized documentation dramatically reduces preparation burden.
Modernization of physical security should be evaluated across:
Security modernization is not an expense line.
It is a resilience investment.
At scale (200+ locations), operational efficiencies and risk reduction compound significantly.
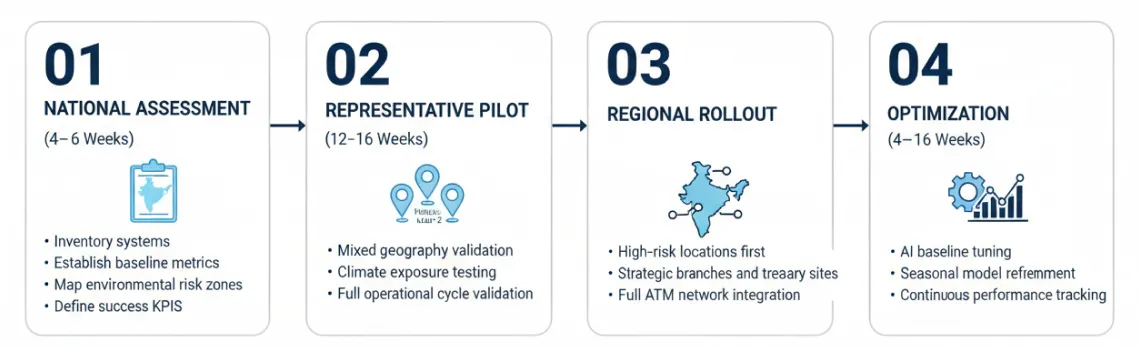
Modernization should follow phased rollout:
Security transformation must be structured not disruptive.
Yes. All device communication is encrypted using AES-256 and secured via TLS 1.3. Access is controlled with MFA and role-based permissions.
Yes. Multi-path communication with automatic failover ensures resilience. Local alarm functionality continues even during temporary connectivity disruption.
By learning location-specific baselines and correlating multiple inputs rather than reacting to single sensor triggers.
The platform integrates with Atigo IoT-based intrusion systems and can be deployed in phased modernization across legacy infrastructure.
Indian banking networks are too large, too distributed, and too environmentally complex to rely on fragmented alarm systems.
Security in 2026 demands:
AIoT Security Intelligence Platforms represent the next phase of banking risk governance.
Modernizing physical security across a distributed Indian banking network requires structured evaluation—not incremental upgrades.
Before initiating vendor discussions, leadership teams should first assess their current readiness across:
The RBI Security Readiness Checklist helps CSOs and Risk Leaders evaluate:
This checklist is designed to be reviewed at CSO level, Risk Committee level, and during internal audit preparation.
to benchmark your current security architecture against 2026 banking expectations.
Atigo is an Indian AIoT safety and security technology company focused on designing systems engineered specifically for Indian operating conditions.
Designed for India’s climate, scale, and regulatory landscape.
Secure. Compliant. Connected. Made in India for India.
India’s trusted security partner since 2013. Made in India manufacturer of 24/7 monitored alarm systems.
© 2013-2025 Atigo Security — A division of Atigo Enterprises Limited
Made in India. Monitored in India.