Yes. While RBI does not explicitly use the term “24/7 alarm monitoring,” its cybersecurity framework and baseline security controls require continuous detection, rapid escalation, and time-bound incident reporting. In practice, this makes professional 24/7 monitoring essential for compliance.
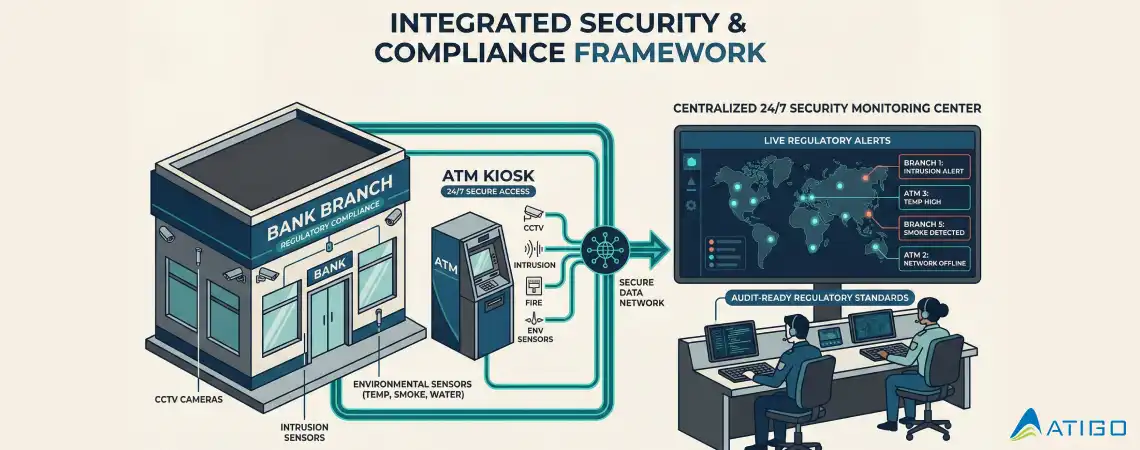
RBI’s cybersecurity framework explicitly includes physical security controls across the entire banking ecosystem—branches, ATMs, vaults, data centers, and IT facilities. Banks must protect not only digital assets but also physical infrastructure that supports financial operations.
This includes power systems, telecom connectivity, environmental conditions, access control, and fire safety systems. These controls must work together as a unified security environment.
RBI baseline controls require banks to implement:
Security incidents must be reported to RBI within 2–6 hours of detection, with follow-up reporting where required.
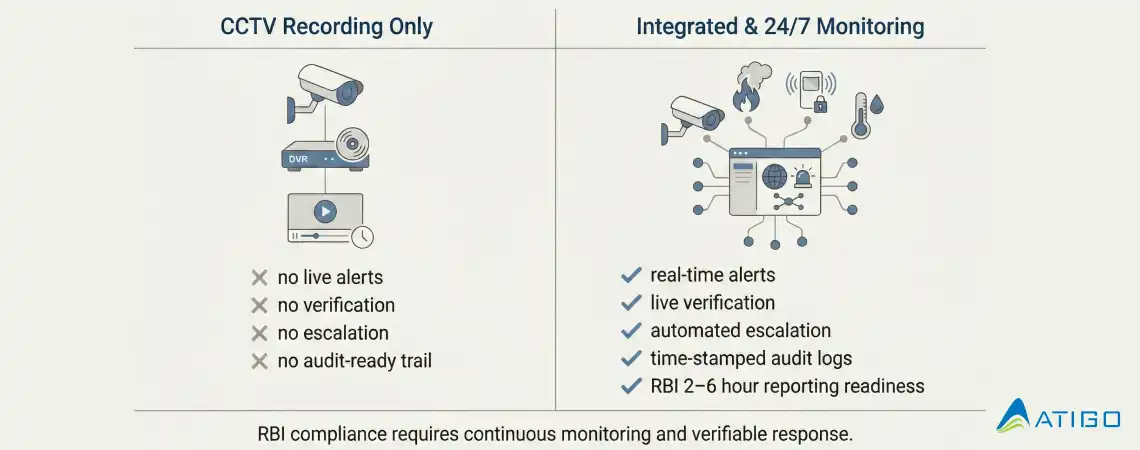
CCTV systems are mandatory, but recording footage alone does not ensure compliance. RBI expects active detection, verification, and response. Unmonitored CCTV cannot detect fires, validate alarms, or trigger timely escalations.
True compliance requires CCTV to be integrated with fire, intrusion, and environmental alarms and monitored continuously.
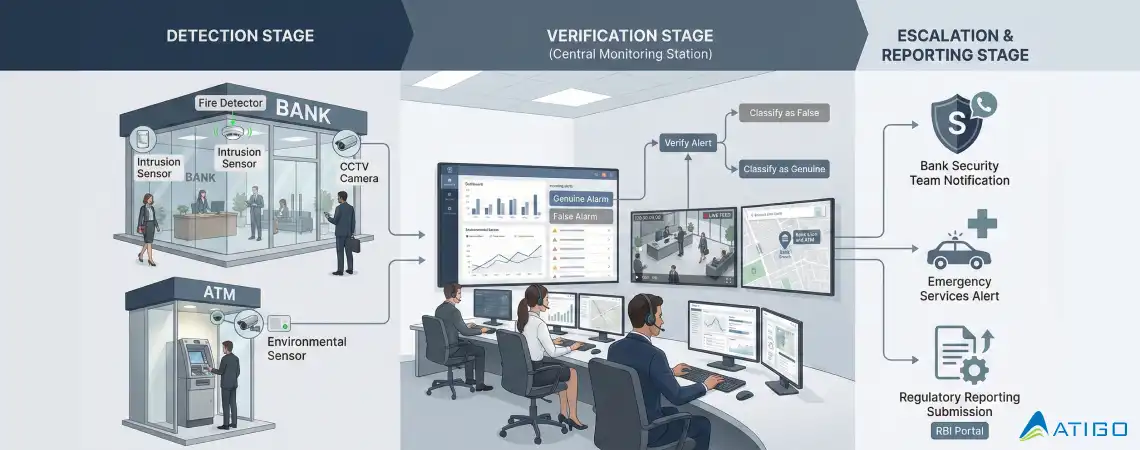
A Central Monitoring Station (CMS) is a 24/7 command center that receives alerts from bank locations, verifies incidents using live video and audio, escalates events to bank officials and emergency services, and maintains detailed audit trails.
Modern CMS operations include redundancy, backup power, disaster recovery monitoring sites, and standardized incident response protocols—critical for meeting RBI timelines.
Most alarm activations are false positives. Without verification, this leads to alert fatigue and delayed responses.
Professional monitoring centers use live video verification, two-way audio, and standardized incident classification to ensure genuine threats receive immediate response while filtering false alarms.
RBI explicitly requires monitoring of environmental conditions such as temperature, smoke, humidity, and water levels. These risks can disrupt banking operations as severely as cyberattacks or physical intrusions.
Fire remains one of the most critical threats to bank infrastructure, especially in server rooms, vaults, and ATM kiosks.
Indian operating conditions high temperatures, extreme humidity, and power fluctuations often cause imported alarm sensors to fail. This creates compliance gaps.
Alarm systems engineered specifically for Indian environments ensure reliable operation across diverse geographies and continuous RBI compliance.
When selecting alarm and monitoring solutions, banks should evaluate:
RBI requires banks to assess and monitor vendor risk.
Key evaluation questions include:
On-Site Systems
Communication Layer
Monitoring Center
Traditional Guard Model
Integrated Monitoring Model
RBI’s framework focuses on detection, response, and recovery. Modern systems now use AI-powered video analytics, predictive maintenance, automated incident correlation, and behavioral anomaly detection to move from reactive compliance to predictive security.
RBI security guidelines clearly indicate that bank security must be continuous, integrated, and verifiable. 24/7 alarm monitoring is no longer optional it is the operational foundation for compliance, resilience, and trust.
Ready to upgrade? Don’t wait for an audit observation.
Click here to access the RBI Alarm Monitoring Framework and download your compliance checklist.
India’s trusted security partner since 2013. Made in India manufacturer of 24/7 monitored alarm systems.
© 2013-2025 Atigo Security — A division of Atigo Enterprises Limited
Made in India. Monitored in India.